NMT历史上的今天
2017年06月13日,中国林科院亚热带林业研究所卓仁英用NMT发表了标题为Overexpressing the Sedum alfredii CuZn Superoxide Dismutase Increased Resistance to Oxidative Stress in Transgenic Arabidopsis的研究成果。

期刊:Frontiers in Plant Science
主题:在转基因拟南芥中过表达景天苜蓿Cu/Zn超氧化物歧化酶提高了对氧化应激的抗性
标题:Overexpressing the Sedum alfredii CuZn Superoxide Dismutase Increased Resistance to Oxidative Stress in Transgenic Arabidopsis
检测指标:Cd2+流速
作者:中国林科院亚热带林业研究所卓仁英、韩小娇、李真
英文摘要
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) is a very important reactive oxygen species (ROS)- scavenging enzyme. In this study, the functions of a Cu/Zn SOD gene (SaCu/Zn SOD), from Sedum alfredii, a cadmium (Cd)/zinc/lead co-hyperaccumulator of the Crassulaceae, was characterized.
The expression of SaCu/Zn SOD was induced by Cd stress. Compared with wild-type (WT) plants, overexpression of SaCu/Zn SOD gene in transgenic Arabidopsis plants enhanced the antioxidative defense capacity, including SOD and peroxidase activities.
Additionally, it reduced the damage associated with the overproduction of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and superoxide radicals (O2 ). The influence of Cd stress on ion flux across the root surface showed that overexpressing SaCu/Zn SOD in transgenic Arabidopsis plants has greater Cd uptake capacity existed in roots. A co-expression network based on microarray data showed possible oxidative regulation in Arabidopsis after Cd-induced oxidative stress, suggesting that SaCu/Zn SOD may participate in this network and enhance ROS-scavenging capability under Cd stress.
Taken together, these results suggest that overexpressing SaCu/Zn SOD increased oxidative stress resistance in transgenic Arabidopsis and provide useful information for understanding the role of SaCu/Zn SOD in response to abiotic stress.
中文摘要(谷歌机翻)
超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)是一种非常重要的活性氧(ROS)清除酶。在这项研究中,表征了景天科植物景天科植物镉(Cd)/锌/铅超积累的Cu / Zn SOD基因(SaCu / Zn SOD)的功能。
镉胁迫诱导了SaCu / Zn SOD的表达。与野生型植物相比,转基因拟南芥植物中SaCu / Zn SOD基因的过表达增强了其抗氧化防御能力,包括SOD和过氧化物酶活性。
此外,它还减少了与过氧化氢(H2O2)和超氧自由基(O2)过量产生相关的损害。Cd胁迫对根表面离子通量的影响表明,过表达SaCu / Zn SOD在转基因拟南芥植物中具有更大的Cd吸收能力。基于微阵列数据的共表达网络表明,Cd诱导的氧化胁迫后拟南芥中可能存在氧化调控,这表明SaCu / Zn SOD可能参与该网络并增强Cd胁迫下的ROS清除能力。
综上所述,这些结果表明,过表达SaCu / Zn SOD在转基因拟南芥中提高了抗氧化胁迫的能力,并为理解SaCu / Zn SOD在响应非生物胁迫中的作用提供了有用的信息。
此外,暴露于Cd下的细胞壁厚度下降导致HE细胞壁中较少的细胞壁键合Cd。因此,Cd诱导的根部特征以及根尖的改变导致了两种生态型苜蓿链球菌对Cd吸收和积累的差异。
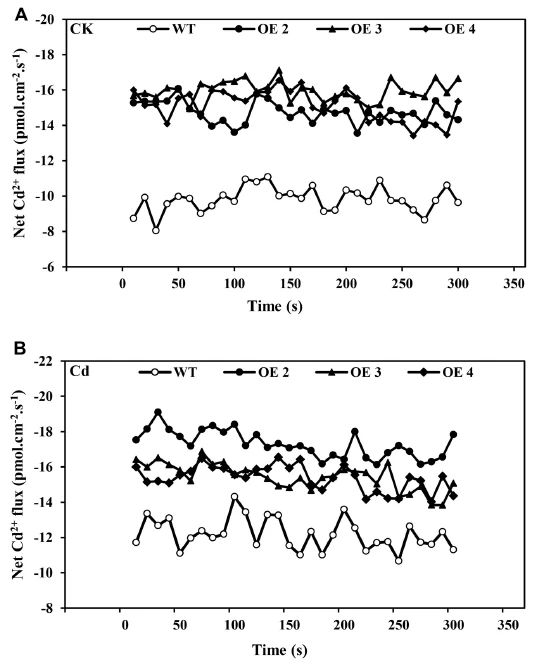
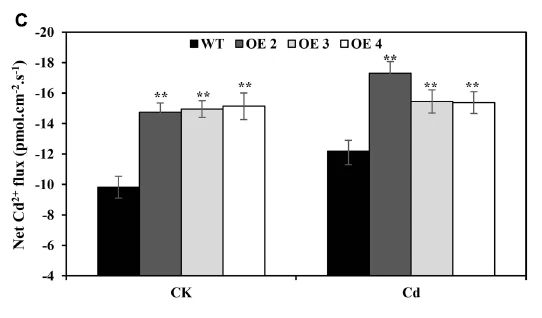
FIGURE 4 | Net Cd2C fluxes. Net Cd2C fluxes in the roots of transgenic (OE2, OE3, and OE4) and WT plants treated without (A) or with CdCl2 stress (B), respectively. The average 300 s net Cd2C fluxes (C) are illustrated to highlight the trend differences. Bars indicate means SD. Asterisks indicate significant differences at p < 0.05 and p < 0.01.
关键词:非损伤微测技术、NMT历史上的今天,Cd 2+流速
